
Parenting!! The first thing that comes to mind when we hear the word parenting is our upbringing by our parents. Is it all about how they took care of us? How did they guide us? What did they do for us? And so on. Parenting involves a wide range of tasks and obligations that vary as the child matures, including providing emotional and physical support, disciplining, socializing, and so forth. Parents have a crucial role in providing deep support and encouragement for their child’s physical, emotional, social, financial, and mental development from birth until adulthood.
Love, affection, and emotional support are the three things that children in this generation most expect from their parents and are essential to their mental and emotional well being. They look to their parents to provide a secure atmosphere and to meet their basic requirements, such as housing, food, and medical care.
Does parenting vary between individuals and cultures? Yes, parenting styles can differ greatly between individuals and cultures. Numerous things can have an impact on them, such as individual experiences, cultural standards, and the distinct needs and personalities of both parents and children. Effective parenting requires balancing love, care, and support to positively impact a child’s mental health, cognitive development, social skills, and overall well-being.
What is Considered Normal Parenting Style?
“Normal” parenting is a broad term that can vary greatly depending on cultural norms, societal expectations, and individual beliefs. However, there are some general principles and practices that are widely recognized and encouraged across different cultures and by child development experts. These practices aim to provide children with a supportive, nurturing, and safe environment that promotes healthy development.
Key Attributes of Conventional Parenting Approaches
1. Providing Basic Needs:
Ensuring that the child has access to adequate nutrition, shelter, healthcare, and safety.
2. motional Support:
Offering love, acceptance, and reassurance to help foster a child’s self-esteem and emotional well-being.
3. Education and Learning:
Encouraging and supporting educational opportunities, intellectual curiosity, and the development of skills and knowledge.
4. Discipline and Guidance:
Implementing consistent and reasonable boundaries to help children learn appropriate behaviors and self-control. This includes teaching consequences for actions, but doing so in a way that is supportive and not harmful.
5. Social Skills:
Teach children how to interact with others respectfully and effectively, understand social norms, and develop empathy.
6. Encouraging Independence:
Allowing children to try things on their own, make decisions, and learn from their successes and failures, appropriate to their age and developmental stage.
7. Moral and Ethical Development:
Guiding children in developing a sense of right and wrong, fairness, and compassion.
8. Respecting Individuality:
Recognizing and nurturing each child’s unique interests, talents, and personality, while also setting appropriate limits.
9. Parental Involvement:
Being involved in the child’s life, showing interest in their activities, and being available to listen and provide guidance.
10. Adaptability:
Adjusting parenting strategies as children grow and their needs change, and being open to learning and seeking support when necessary.
Understanding Parental Norms: Is Our Parenting Style Good?
The question of whether the way we parent is “normal” is complex and multifaceted, largely because parenting practices vary significantly across cultures, communities, and individual families. The concept of “normal” in parenting can be influenced by many factors, including cultural norms, societal expectations, psychological theories, and personal beliefs and values. Here are some key points to consider in understanding the diversity and norms in parenting:
1. Cultural Differences:
Parenting practices can differ greatly from one culture to another. What is considered normal in one culture might be seen as unusual or even unacceptable in another. For example, co-sleeping with children is common in many Asian cultures but less so in many Western cultures.
2. Changing Norms:
Ideas about what constitutes normal parenting have changed over time and continue to evolve. Practices that were common in the past, such as corporal punishment, are now discouraged or even prohibited in many places. Conversely, approaches like positive reinforcement and empathetic parenting have gained popularity.
3. Individual Differences:
Within any given culture, there’s a wide range of parenting styles. These styles can be influenced by a parent’s upbringing, education, personality, and the unique needs of each child. What works for one family may not work for another.
4. Societal and Economic Influences:
Socioeconomic factors also play a significant role in shaping parenting practices. For example, the availability of parental leave, childcare options, and community support can significantly impact how parents raise their children.
5. Psychological Perspectives:
Psychologists have identified different parenting styles, such as authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, and uninvolved. Each style has different effects on children’s development, and there’s ongoing research into the outcomes associated with each.
6. Globalization and Information Exchange:
With the advent of the internet and social media, parents have more access to information and parenting practices from around the world. This can influence perceptions of what is normal and encourage a more eclectic approach to parenting.
How Do Mothers and Fathers Differ in Their Approach to Parenting?
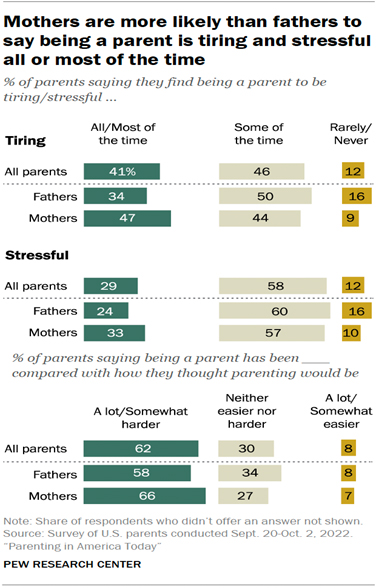
As per the PEW Research Centre, the chart indicates that compared to fathers, mothers are more inclined to identify themselves as being overprotective and prone to conceding to their children’s demands prematurely.
Why is There a Need for Change?
In many Indian families, there’s either a strict regime covering play, study, and sleep times with punishments for not following the rules, or there’s no structure at all. This lack of balance is a problem. While most of us are well-cared for materially, something crucial is missing: emotional nurturing. A common agreement is emerging: Indian parents need to prioritize their children’s well-being over concerns about societal judgment if they seek help for early signs of troubling behavior. The focus seems to be more on earning a living than on nurturing family bonds and happiness.
Shouldn’t we also focus on instilling strong moral and ethical values in our children to help them positively contribute to society as they grow? Unfortunately, confidence-building, encouragement, and deep conversations are often missing in Indian households. There’s a strong desire for children to excel academically and achieve greatly, but it’s time for a shift. We need to change to protect our youth and restore our community’s pride.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that there is no “one-size-fits-all” approach to normal parenting. What is considered normal or acceptable can differ widely between cultures and even within the same community or family. The effectiveness of different parenting practices can also vary depending on the individual child’s temperament, the parents’ personalities, and other situational factors.
What’s most important is that children are raised in a loving, supportive environment that meets their physical, emotional, and developmental needs of the child into a well-adjusted, capable, and happy individual. It’s also beneficial for parents to remain open to learning and adapting their parenting practices as they gather new information and as their children grow and change.
FAQs
1. Which parenting style is good?
Authoritative parenting is considered the most healthy and effective style. It balances warmth and boundaries, promoting confident, responsible adults. They listen to their child’s input and provide positive feedback.
2. What do you understand by parenting styles?
Parenting styles refer to the various approaches and strategies used to raise and interact with their children. These styles influence how they communicate, set rules, express affection, and provide guidance. Different parenting styles can have a significant impact on a child’s emotional, social, and cognitive development.
3. How do I choose parenting styles?
Choosing a parenting style involves understanding your child’s unique personality, reflecting on your values and expectations, and considering the outcomes you hope to foster in your child’s development. It’s also important to be flexible, as different situations or stages of your child’s life might require different approaches. Engage in self-reflection and, if possible, discuss parenting strategies with other caregivers in your child’s life to ensure consistency and support. Ultimately, the parenting style should foster a secure, encouraging, and nurturing environment, allowing your child to grow into a well-rounded and capable individual.
4. What is a positive parenting style?
Positive parenting is a style centered on developing a strong, deeply committed relationship between parent and child based on communication and mutual respect. Positive parenting focuses on teaching and guiding children, rather than controlling them through punitive measures. Positive parenting emphasizes empathy, encouragement, and problem-solving.
- Encouragement: Praising effort and progress rather than just outcomes.
- Active Listening: Taking time to listen to your child’s feelings and thoughts.
- Setting Realistic Expectations: Recognizing age-appropriate abilities and adjusting expectations accordingly.
- Problem-Solving Together: Involving your child in finding solutions to challenges.
- Modeling Positive Behavior: Being a role model for kindness, empathy, and respect.
5. What are the best parenting techniques?
The “best” parenting techniques can vary depending on your child’s needs, personality, and the specific challenges you face together. Here are some universally recognized techniques that are considered effective across various circumstances and developmental stages.
- Setting clear, consistent boundaries and rules.
- Positive reinforcement by rewarding children for good behavior rather than punishing them for bad behavior.
- Active listening and being empathetic.
- Modeling behavior as children learn a lot by imitation.
- Problem-solving skills with guidance, support their ability to navigate challenges independently as they grow.
- Empathy and emotional awareness are crucial for their social and emotional development.
- Spend quality time as it strengthens the relationship and communication.
- Educational support by showing interest in their academic life and helping them to utilize their strengths while addressing any challenges they face.
- Be willing to adapt your parenting style as your child grows and as their needs change.






Social